The question of how many steaks emerge from a beef cow is complex to answer.
Various characteristics of the animal including its genetic background and feed intakes alongside preparation processes influence the production of steak cuts together with their overall quality and their number.
The article investigates steak yield variables while detailing the complete process of beef yield transformation from live cattle to retail cuts.
How many steaks are in a cow?
Several influencing elements determine how many steaks you will eat. The process does not involve evenly partitioning a cow into sections. The yield depends on multiple factors which include:
- Steak yield depends heavily on how breed, genetics and age, frame size and gender affect animals.
- Finishing a cow on grass or feed causes small changes to its muscle structure and how fat spreads throughout its body.
- Allowing bones in or removing them from the cuts remains important in addition to the precise sequence of cut preparation during butchering and processing.
Every element both changes steak quantity and modifies dimensions alongside improving or diminishing their tenderness and quality.
The number of steaks depends on the breed of the cattle
Each type of cattle shows unique patterns for its muscle development. The majority of muscular domestic cattle breeds produce abundant high-quality cuts which compete with other cattle breeds that yield more ground meat and suitable roasting cuts.
Genetic factors determine the steak count
Heritage factors control both muscle fiber structures and internal fat patterns. Animals with high genetic quality tend to generate better quality steaks in their yield.
Cow age influences the number of steaks
The aging process strongly determines how meat develops tenderness while determining muscular growth through time. The age of the cow decides whether the steaks will be tender because younger animals make better products than older animals that create tougher tissue leading to different carcass divisions.
Frame size influences the number of steaks
The usable meat provided by cows directly corresponds to their physical sizes. The substantial body of larger frame cows yields greater meat weight however the cut proportions depend upon other influencing variables.
The gender division of animals affects steak quantity
The ratio of muscle to fat between steers and heifers determines how many steaks are obtained during processing as well as the steak texture attributes.
Steak quantity as well as meat quality depends on what food cows eat
The nutritional regimen together with finishing type either on grass or grain significantly affects taste components and fat patterning in the meat.
Grass-Finished vs Grain-Finished
Steers that are raised on grass exhibit strong flavor characteristics together with a lean meat structure although steers that feed on grains develop enhanced marbling that delivers both flavor and tenderness.
Processing influences the number of steaks
The complete process of handling cows leads to major changes in the end product quality. The butcher’s methods which include using bone-in or boneless cuts as well as selecting roasts instead of steaks influence the overall number of steak cuts available.
Roasts or Steaks?
The number of portions will change based on whether the meat cutter gives priority to roast cuts or smaller steak cuts. Every method results in distinctive benefits regarding both flavor and texture quality.
How thick do you want each steak?
The entire steak cutting process depends heavily on steak thickness. The production of few steaks from a carcass through thick cuts results in superior juiciness but the number of portions increases when cutting steaks thin.
How much beef do you get from a cow?
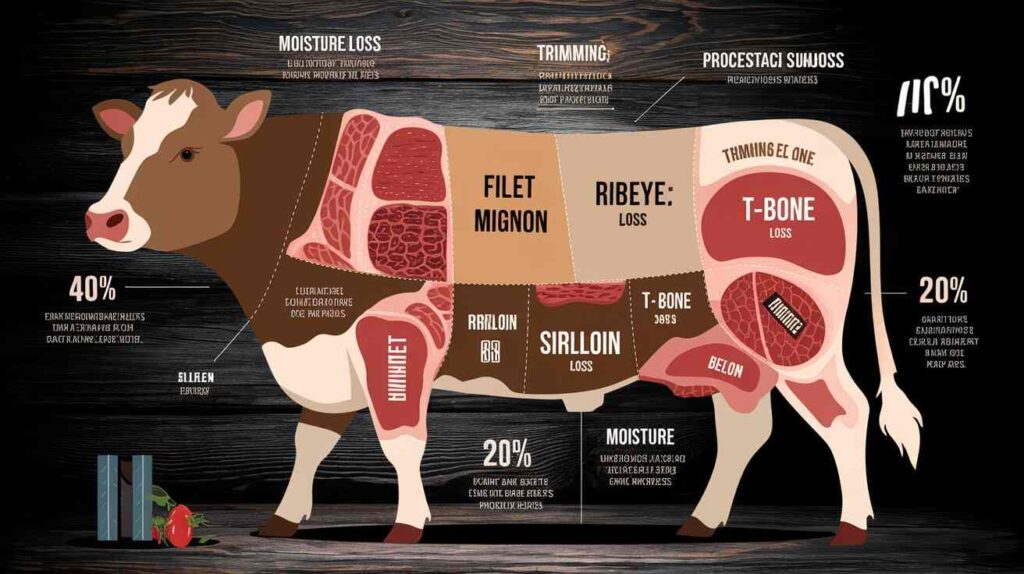
The transformation of live beef weight into packaged retail cuts goes through a comprehensive series of steps for complete beef yield comprehension. The live weight of a beef steer usually reaches about 525 kilograms. Some portions of total beef weight do not transform into retail meat products.
Four hundred percent of live weight gets lost during the first processing stage where technicians perform bleeding tasks while removing skin and head structures along with hooves and internal organs. The remaining weight amounting to 60% of the total constitutes the “hanging weight” specification.
After retail cuts the yield continues to grow. Rates of moisture loss and fat and bone trimming applied to the rail product reduce the overall weight by an additional 20%. The total live weight of 525 kilograms for a steer typically leads to 250 kilograms of beef ready for retail consumption. Different types of cuts receive their portion from this yield:
- Half of total weight gets converted into ground beef products.
- A quarter of the meat may be designated specifically for roasts together with similar cuts.
- The remaining quarter enables processors to cut steak products from the meat.
Your end results and choices during processing determine the significant variability seen in the steak quantity obtained from a beef animal.
Prime vs Choice vs Select
Beef quality grades Prime, Choice and Select can be used to determine both meat tenderness levels as well as fat distribution and market prices as consumers show varying grade preferences. The superior quality of Prime cuts drives premium pricing but consumers can achieve premium flavors from selecting either Choice or Select grades when they receive proper cooking treatment.
The selection of beef grade determines cut distribution across different products because premium cuts normally appear as steaks whereas lower-grade pieces become roasts and ground beef.
The Cuts You Can Expect
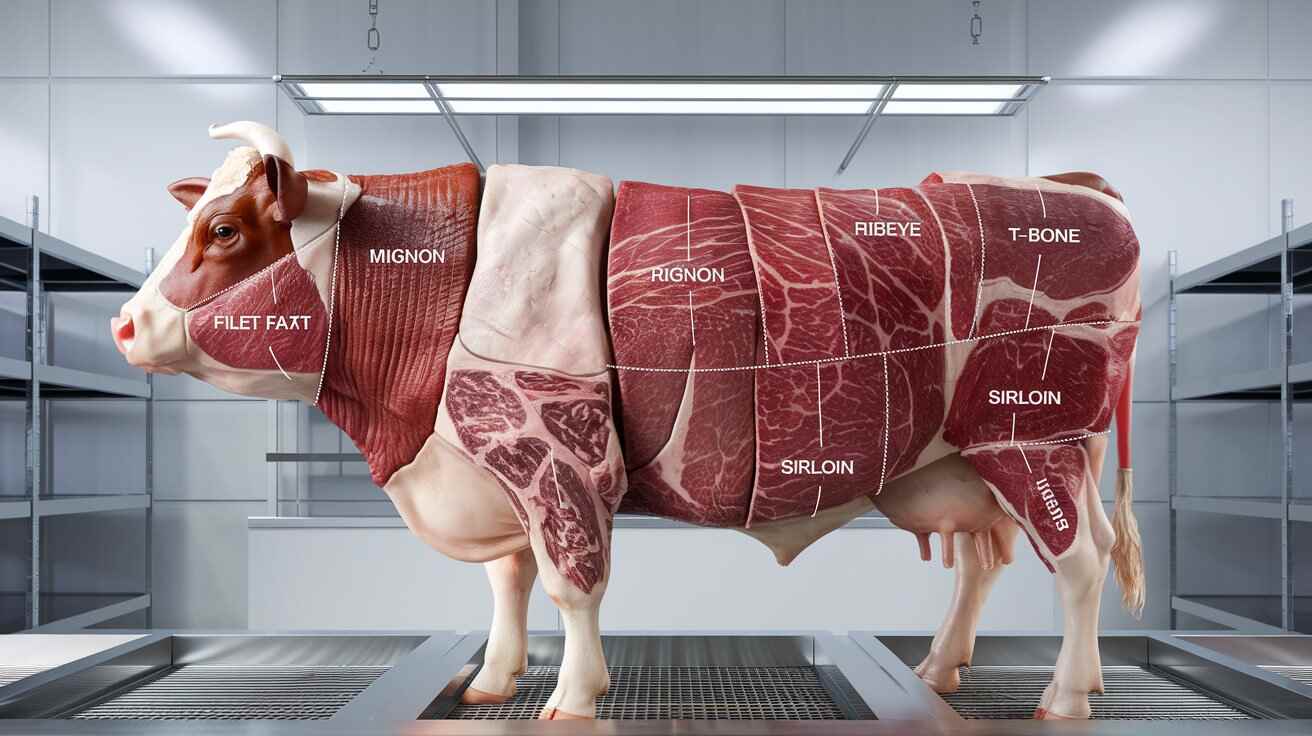
The purchase of a beef cow includes more than just steaks because the carcass get divided into multiple cuts which work well for distinct culinary methods and taste preferences. These are the main steak cuts prepared for purchase along with their distinctive characteristics:
Filet Mignon
Primarily considered the best piece of beef meat is Filet Mignon. People consider this cut for its delicate and buttery tenderness. The steak delivers a refined eating experience with minimal flavor intensity.
When prepared correctly this cut achieves quick cooking time and retains its juices during preparation. Special occasions demand this premium cut which usually serves as a celebration food.
Ribeye
Consumers know Ribeye for its intense rich taste characteristics. The steak contains a thick fat distribution which transforms into rich content inside the meat during cooking. The beautiful meat marbling throughout the cut enhances its juiciness and tastiness during each mouthful.
You should use this cut for high-temperature grilling or pan-searing because of its exceptional performance in these cooking methods. People who enjoy steaks typically opt for ribeye due to its rich savory qualities.
New York Strip
The New York Strip possesses a stable texture combined with excellent meat quality. The steak provides a pleasing eating experience from its great texture while balancing its inner tender meat with its chewy consistency.
Despite its lean appearance, the New York Strip keeps a strong distinctive taste. The cut works perfectly as an ingredient both on the grill and in hot skillets. People select steak as a popular option since it delivers good results no matter the cooking method.
T-Bone
The T-Bone steak stands out because it offers two different cuts from a single meat piece. One end of the steak shows tender filet while the other side presents delicious strip meat. The two different textures from the combined cuts appear in a single piece.
You should cook this steak on the grill at medium-rare doneness. T-Bone stands out as the perfect steak option for people who prefer different tastes in a single steak.
Porterhouse
The porterhouse variant of steak provides a large tenderloin area along with the features found in T-bone. Simply getting a T-Bone allows you to experience a flavorful strip meat and a generous part of tenderloin at the same time.
A family dinner serves the Porterhouse steak perfectly since it offers two sections for everyone at the table. The two sections of the cut deliver both savory taste notes together with tender meat texture. Steak enthusiasts tend to choose this cut as a top-quality selection.
Sirloin
Sirloin steak maintains a reputation for having lean meat with robust taste. Its texture remains firm compared to highest quality steak cuts. The meat type adapts well to many different cooking methods such as barbecue and pan-searing. You get dependable satisfaction from sirloin when you need a meal in a hurry. The meat meets both taste quality and budget needs.
Flank Steak
Cattle supply flank steak by removing it from the abdominal muscle areas. The meat possesses lean qualities along with a firm yet somewhat fibrous texture. Marination of steak achieves two benefits: it makes the meat tender while also improving its taste.
The proper cooking method for this cut involves quick high-temperature exposure while the meat should be sliced thinly in a direction across the muscle fibers to achieve the best results. The popularity of stir-fries and fajitas makes this cut a suitable choice for these dishes.
Skirt Steak
The strong beef attributes of Skirt steak make it highly sought after by meat lovers. The particular shape of this cut allows it to cook in a short time. Marinating this cut of beef is essential for creating tenderness while it delivers improved flavors. With correct preparation the result is both tender and juicy steak. This steak commonly enters taco preparations and various Latin food creations.
Hanger Steak
Butchers prefer the “butcher’s cut” name for hanger steak because they admire it especially well. The deep savory flavor of this cut distinguishes itself from other meat cuts on the market. The result is natural tenderness after cooking this meat at medium-rare temperature levels. The distinctive flavor of this steak becomes more prominent after basic seasoning. Many consider it a hidden gem among steak cuts.
Flat Iron Steak
Flat Iron steak has recently gained popularity among people who enjoy meat. This steak has gained fame among meat enthusiasts because of its exceptional tenderness along with rich taste.
This steak distributes heat equally during cooking because of its excellent marbling and has well-distributed meat fibers. Consumers can obtain high-quality meat at reasonable prices because Flat Iron steak provides a favorable pricing-quality equation. Flat Iron steak offers an excellent quality cut that comes at an economical price point.
Chuck Eye Steak
For a wallet-friendly steak option Chuck Eye offers satisfactory taste to customers. The chuck eye originates from the identical region as ribeye thus providing matching flavor characteristics.
The steak requires fast cooking at high temperatures for optimal results. The steak maintains its juiciness when prepared with the right cooking methods. Eliminating some costs from the steak price creates this practical choice for budget-minded beef eaters.
Round Steak
Steak derived from the rear leg of the animal is classified as round steak. When cooked without due attention it becomes tough because it naturally remains less tender than alternative meat cuts.
Braising or slow cooking allows round steak to become tender through soaking time. Meat in stews and casseroles acquires excellent flavor absorption. People favor round steak because it delivers a rich straightforward taste.
Cube Steak
Mechanical tenderization increases the tenderness of cube steak. The mechanical processing results in softening of the meat with improved chewing characteristics.
People commonly prepare chicken-fried steak by using this cut of meat. Due to its budget-friendly price point this cut offers flexibility during food preparation. Many enjoy cube steak for its comfort-food appeal.
Tri-Tip
A triangular section known as Tri-Tip originates from the bottom part of the sirloin cut of beef. The cut is famous due to its intense robust flavor which combines subtle smokiness.
The grilled or roasted preparation method proves suitable for this specific cut. When cooked with proper technique Tri-Tip maintains its moist quality. The distinctive structure enables proper size divisions of this cut.
Tomahawk Steak
The remarkable appearance of the Tomahawk steak stems from its handle-sized bone extension. This meat starts as a ribeye but goes beyond its basic form with superior presentation quality.
The grilled Tomahawk steak delivers superior taste quality with tenderness along with its juicy consistency. This massive piece of meat creates a remarkable visual impression suitable for all dining activities. Many choose the Tomahawk for both its taste and its impressive look.
Should You Buy a Whole Cow or a Half Cow?
Your buying decision involves evaluating both your eating habits and your refrigerator storage space as well as which meat pieces you want to prepare. While bulk purchases can provide various cuts at reduced costs you need to develop space to store them while also managing the time between buying and eating.
Homeowners must decide between whole cows or half cows based on their beef eating pace along with their freezer capabilities and their preference for premium meat cuts against ground beef and roasts.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many steaks are in a whole cow?
Steak cuts from a whole cow reach a total of 150 pieces. The variety of steak cuts depends on both the type of breed and the specific butchering technique.
How many tomahawks are in a cow?
Every cow yields two tomahawk steaks which are produced from both sides of the rib section.
How many kg of steak in a cow?
A single cow yields between 50–70 kilograms of steak depending on its dimensions and meat processing techniques.
How many steaks in a bull?
A bull produces approximately 150 steak cuts because its flesh is lean but tends to be tougher than heifer or steer meat.
Can you butcher a 7-year-old cow?
A 7-year-old cow provides meat which requires slow-cooking preparations because its texture tends to be tougher.
How long is a cow pregnant?
Cows bear young after 280–285 days that compose a 9-month pregnancy cycle.
What is the best age to slaughter a cow?
The most suitable time for deeming cattle ready for slaughter falls between their eighteen to twenty-four month period because their meat achieves best tenderness while retaining its flavor.

